Stainless Steel Grades
If you ask which one is the most popular type of metal in the world, absolutely speaking, it is stainless steel. You can see it everywhere in daily life or industrial life. Such as Kitchenware or culinary tools, kitchen sinks, surgical tools, bridges, buildings, roofs, and automotive bodies or parts. It has an incredibly wide range of uses. Even aerospace benefits from its strength and unique traits. What makes stainless steel so special?
Unlike ordinary steel, as its name speaks, stainless steel is not prone to corrosion. It means it is not rust. Let us further understand what stainless steel is. How Many Stainless Steel Grades. and what is used for?
What is Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a generic term. It usually refers to a range of various iron-based alloys that contain 10.5 % of chromium or more. When we add materials of Mo, C, Ni, and Mg, stainless steel is created.
All stainless steels have a high resistance to corrosion. This is because there is a naturally occurring chromium-rich oxide film formed on the surface of the steel. The film is adherent to the metal surface and protective in corrosive media. This is suit different applications.
Besides the resistance to corrosion, stainless steel is heat resistant. Stainless steels are recyclable and so easy to sterilize. It is the perfect material to use for the foodservice industry. It is also poor conductors of electricity. So it is safe to use.
What is Stainless Steel Grades
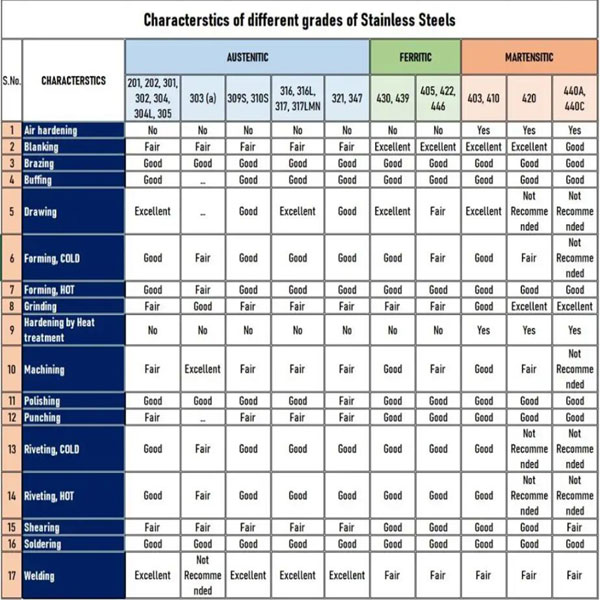
There are many classification methods for stainless steel types. The classification according to the metallographic structure is the most common. The most common Stainless Steel Grades are austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel, duplex stainless steel, precipitation hardening stainless steel.
1—Austenitic
The austenitic type refers to stainless steel with an austenite structure at room temperature. It is the most common stainless steel type. Compared to other materials, they usually contain high content of chromium, as well as molybdenum and nickel. This makes them more resistant to corrosion. It is considered the strongest among the stainless steel types and Has more applications.
When steel content is 18% Cr, 8%~10% Ni, and about 0.1% C, it has a stable austenite structure. Austenite types are non-magnetic unless they are cold worked.
Austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel includes the famous 18Cr-8Ni steel (that is, 304). And on this basis, the high Cr-Ni series steel was developed by adding Cr and Ni content and adding Mo, Cu, Si, Nb, Ti, and other elements.
Austenitic Stainless Steels 300 Series Stainless (ANSI Equivalent)
- CF16F (303)
- CF8 (304)
- CF3 (304L)
- CH20 (309)
- CK20 (310)
- CF8M (316)
- CF3M (316L)
The main Applications: Medical, Mining, Petrochemical, Food & dairy, Automotive, Valves
Common Types:
Grade 304 Stainless Steel: It is the widest used in the market. Especially in industrial piping, kitchen equipment. Good Heat resistant. Strength against chemicals and chlorides.
Grade 316 Stainless Steel: The second most common stainless steels are 316 Stainless Steel. It has the same physical and mechanical properties as the 304. It has stronger corrosion-resistant. The producing product is more used in saltwater environments.
2—Ferritic
Ferritic type Stainless steel is mainly composed of ferrite in the application.
The chromium content is between 11% and 30%. It has a centered cubic crystal structure.
This stainless steel generally does not contain nickel. Sometimes it will contain a small amount of Mn, Ti, Nb, and other elements. It is like low-carbon steel. But the difference is that it is magnetic and has a higher chromium content.
It has the characteristics of large thermal conductivity, small expansion coefficient, good oxidation resistance, and excellent stress corrosion resistance. It is mostly used to manufacture parts that are resistant to atmospheric, water vapor, water and oxidizing acid corrosion.
However, this type of stainless steel has disadvantages. Such as poor plasticity, reduced plasticity, and corrosion resistance after welding. This shortage limits its application.
Common Types:
Grade 430 Stainless Steel: Compared to the austenitic types, it has a strong resistance against nitric acid. Austenitic types do not contain nickel. Price is more affordable. Grade 430 is the better choice for grills for barbeques.
Grade 434 Stainless Steel: These are the stronger alternative to Grade 430. It is slightly stronger and better for high-temperature applications. It does not react to heat treatment.
3—Duplex–Austenitic/Ferritic Stainless Steel Grade
The duplex stainless steel is a combination of austenite and ferrite structures stainless steel. About half to half. In the case of low C content, the Cr content is 18% to 28%. The Ni content is 3% to 10%.
Some steels also contain alloying elements such as Mo, Cu, Si, Nb, Ti, and N. It combines the characteristics of austenitic and ferritic stainless steel.
But compared with ferrite, it has higher plasticity and toughness. There is no brittleness at room temperature. Intergranular corrosion resistance and welding performance are significantly improved.
At the same time, it also maintains the brittleness of ferritic stainless steel at 475°C and high thermal conductivity. It has superplasticity Features.
Compared with austenitic stainless steel, it has high strength and improved resistance to intergranular corrosion and chloride stress corrosion.
Duplex stainless steel has excellent pitting corrosion resistance. It is also nickel-saving stainless steel.
The duplex stainless steel type both have the strength and flexibility needed for industries. Such as chemical engineering, shipbuilding, pulp and paper, and even the petrochemical industries. It has improved corrosion resistance as well and is more ductile compared to ferritic.
The duplex stainless steel type is divided into three groups based on its corrosion resistance: the standard duplex, super-duplex, and lean duplex grades.
Austenitic/Ferritic Stainless Steels Common Type
2205 Series
- X2CrNiMoN22-5-3
Main Applications:
Chemical processing & storage.Oil & gas exploration.Cargo tanks.Food & dairy.Marine Accessories
4—Martensitic
Martens stainless steel is a kind of stainless steel whose mechanical properties can be adjusted by heat treatment. In other words, it is a kind of hardenable stainless steel.
Compared with other stainless steel grades, it is not high corrosion-resistant. But they are considered to be very hard and sturdy types. The performance is very like the ferrite grade. But the carbon content is higher.
This type is mainly used to make knives, steam turbine blades, tableware, and surgical instruments.Automotive.Machine tool.Food & dairy.Firearms
According to the difference in chemical composition, martensitic stainless steel can be divided into martensitic chromium steel and martensitic chromium-nickel steel.
Typical grades are Cr13 type, such as 2Cr13, 3Cr13, 4Cr13, and so on.
- CA15 (410)
- IC 416 (416)
- CA40 (420)
- IC 431 (431)
- IC 440A (440A)
- IC 440C (440C)
Common Type:
The Grade 420 Stainless Steel type is resistant to mild acids, water, and food compounds. Compared to austenitic and ferritic types, this is not as resistant to chemicals.
5–Precipitation Hardening (PH)
Precipitation hardening stainless steel is a type of stainless steel. It refers to stainless steel that precipitates different types and quantities of carbides, nitrides, carbonitrides, and intermetallic compounds by adding different types and quantities of strengthening elements.
It is a type of high-strength stainless steel. It does not only improve the strength of steel but also maintains enough toughness. It is also called PH steel
Precipitation hardening stainless steel has high strength, high toughness, high corrosion resistance, high oxidation resistance, and excellent formability, weldability properties.
Main Applications: It is widely used in cutting-edge industry and civil industry. Military.Medical.Machine tool.Hand Tools.Aerospace. For example, PH 17-4. It can be used to make structures that require corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and high strength below 370°C.
Typical Grade: 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb,0Cr17Ni7Al,0Cr15Ni25Ti2MoVB
14-4 PH Series
- AMS5340
15-5 PH Series
- ASTM A 747 CB 7Cu-2
- AMS 5346
- ASM 5347
- ASM 5356
- AMS 5357
- AMS 5400
17-4 PH Series
- ASTM A 747 CB 7Cu-1
- AMS 5342/5344
- AMS 5343
- AMS 5355
- MIL-S-81591 IC -17-4
Stainless Steel Grade Casting and Applications
1– 304
It is also referred to as A2 stainless. It is the most widely used stainless steel casting material. Austenitic stainless steel with Ni content of more than 8%, food-grade alloy. stainless steel 304 castings can be used in environments where the air is less corrosive.
Applications: Medical, food industry, mechanical equipment, pipe industry, automotive industry, chemical industry.
2–304L
This grade has slightly lower mechanical properties than SS 304 grade. But it is still widely used in casting for its versatility. Austenitic stainless steel with Ni content more than 8%. Food grade alloy. It can be used to cast stainless steel components for both household and commercial applications.
Applications: Food, chemical, medical, plumbing, etc.
3–316
The second most common austenite steel. It is also referred to as A4 stainless.
SS316 is used primarily for its increased resistance to corrosion. The content of more Ni is more than 10%. For its higher Ni content, 316 stainless steel castings have better corrosion resistance than 304 stainless steel castings. Stainless steel 306 castings are better suited for the marine environment with relatively harsh air conditions or chemical materials.
Applications: Marine Parts
4–316L
Lower carbon content than 316 stainless steel. It has better resistance to stress-corrosion cracking. The mechanical properties are close to SS 304 and ss 316. letter of L represents lower carbon content. It makes the material more ductile, has good welding performance. It has more reliable corrosion resistance. The price is higher than the same grade.
Applications: Food, chemical, medical, plumbing, etc.
5–410 416
Series 400 belongs to martensitic stainless steeL. It is characterized by high strength, good processing performance, and high heat treatment hardness. It does not contain Ni. So the corrosion resistance is weak.
Applications: Auto parts, tools, knives, etc
6–PH17-4
The most common precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel. The content is about 17% chromium and 4% nickel. Good corrosion resistance. It has the highest strength in the stainless steel series. It is usually used for products and parts that are not easy to deform.
Applications: Military, medical, mechanical components, machine tools, turbine blades, etc.
7–2205
Duplex stainless steel 2205 is composite stainless steel consisting of 22% chromium, 2.5% molybdenum, and 4.5% nickel-nitrogen. It has high strength. Good impact toughness. good overall and local resistance to stress corrosion.
Applications: Sporting, pump & valve industry, etc.
Chemical Composition for Stainless Steel Casting
| Grades | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Mo |
| 304 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.045 | 18 ~ 20 | 8 ~ 11 | – |
| 304L | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.035 | 18 ~ 20 | 8 ~ 12 | – |
| 316 | ≤0.08 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.045 | 16 ~ 18 | 10 ~ 14 | 2 ~ 3 |
| 316L | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.045 | 16 ~ 18 | 10 ~ 14 | 2 ~ 3 |
| 410 | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.040 | 11 ~ 13.5 | ≤0.6 | – |
| 416 | ≤0.15 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.25 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.060 | 12 ~ 14 | ≤0.6 | – |
| 17-4 ph | ≤0.07 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.040 | 15.5 ~ 17.5 | 3 ~ 5 | – |
| 2205 | ≤0.03 | ≤1.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.040 | 21 ~ 24 | 4.5 ~ 6.5 | 2.5 ~ 3.5 |
Conclusion
When choosing the right stainless steel grade or for casting, it is important to understand what your requirements are. And to analyze which type suits your needs.
Stainless steels are not only strong against chemicals or acidic environments. But the great mechanical and machining features. That is why it has been so widely used all over the world.
Hopefully, this article would help you make that final choice.
If you have stainless steel grade casting product requirements. You can contact JC Casting freely. Leave a message or email us at info@jccasting.com
